Out of the box, Camunda Tasklist supports four different kinds of task forms:
- Embedded Task Forms: HTML-based task forms, displayedembedded within Tasklist.
- : Like embedded task forms, butgenerated from XML metadata within the BPMN 2.0 XML.
- External Task Forms: The user is directed to anotherapplication to complete the task.
- : If no task form exists, a generic formis displayed to edit the process variables.
When embedding the process engine into a custom application, you can integrate the process engine with any form technology such as [JavaServer Faces][jsf-task-forms], Java Swing, JavaFX, REST-based JavaScript web applications and many more.
Embedded Task Forms
Embedded task forms are HTML and JavaScript forms which can be displayed directly within Tasklist. We provide more information about the creation of embedded forms in our Embedded Task Forms Reference.
To add an embedded form to your application, simply create an HTML file and refer to it from a or a StartEvent in your process model. For example, you can create a FORM_NAME.html file containing the relevant content for your form, e.g., a simple form with two input fields:
The file containing the form can be referenced in two ways:
- app:: Add the file to your development project in a folder src/main/webapp/forms. The HTML file will be packaged into your deployment artifact (typically a WAR archive). During runtime it will be loaded from there.
- deployment:: The file is part of your deployment (e.g., ), which means that it is stored in the Camunda database. It can then be loaded from there. Note that this allows versioning of your form alongside the process model.
To configure the form in your process, open the process with the Camunda Modeler and select the desired or StartEvent. Open the properties panel and enter (orembeddedforms/FORM_NAME.html) as Form Key. The relevant XML tag looks like this:
<userTask id="theTask" camunda:formKey="embedded:app:forms/FORM_NAME.html"name="my Task">
Generated Task Forms
The Camunda process engine supports generating HTML task forms based on Form Data Metadata provided in the BPMN 2.0 XML. Form Data Metadata is a set of BPMN 2.0 vendor extensions provided by Camunda, allowing you to define form fields directly in the BPMN 2.0 XML:
Form metadata can be graphically edited using the .
This form would look like this in Tasklist:
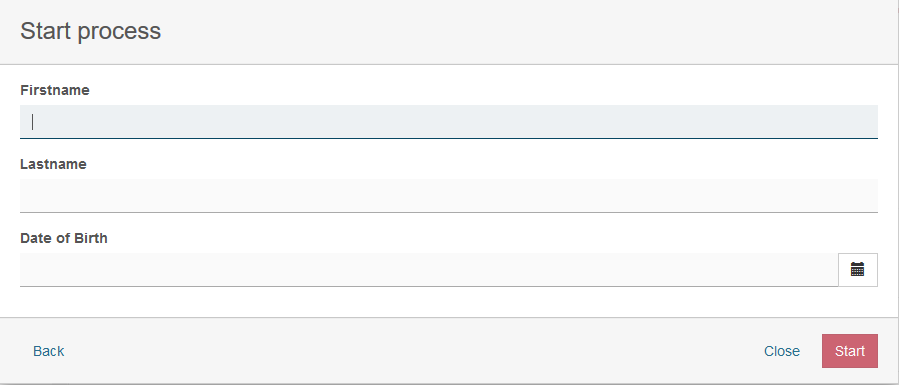
As you can see, the <camunda:formData … /> element is provided as a child element of the BPMN <extensionElements> element. Form metadata consists of multiple form fields which represent individual input fields where a user has to provide some value or selection.
A form data can have following attributes:
A form field can have the following attributes:
string
long
boolean
enum
|defaultValue|Value to be used as a default (pre-selection) for the field.
Form Field Validation
Validation can be used for specifying frontend and backend validation of form fields. Camunda BPM provides a set of built-in form field validators and an extension point for plugging in custom validators.
Validation can be configured for each form field in the BPMN 2.0 XML:
<camunda:formFieldid="firstname" name="Firstname" type="string"><camunda:validation><camunda:constraint name="maxlength" config="25" /><camunda:constraint name="required" /></camunda:formField>
As you can see, you can provide a list of validation constraints for each form field.
The following built-in validators are supported out of the box:
Applicable to all types. Validates that a value is provided for the form field. Rejects 'null' values and empty strings.
<camunda:constraint name="required" />
|minlength|
Applicable to string fields. Validates the minimum length of text content. Accepts 'null' values.
<camunda:constraint name="minlength" config="4" />
|maxlength|
Applicable to string fields. Validates the maximum length of text content. Accepts 'null' values.
<camunda:constraint name="maxlength" config="25" />
|min|
Applicable to numeric fields. Validates the minimum value of a number. Accepts 'null' values.
|max|
Applicable to numeric fields. Validates the maximum value of a number. Accepts 'null' values.
<camunda:constraint name="max" config="10000" />
|readonly|
Applicable to all types. Makes sure no input is submitted for the given form field.
<camunda:constraint name="readonly" />
Camunda BPM supports custom validators. Custom validators are referenced using their fully qualified classname or an expression. Expressions can be used for resolving Spring or CDI @Named beans:
A custom validator implements the org.camunda.bpm.engine.impl.form.validator.FormFieldValidator interface:
public class CustomValidator implements FormFieldValidator {// ... do some custom validation of the submittedValue// get access to the current executionDelegateExecution e = validatorContext.getExecution();// get access to all form fields submitted in the form submitMap<String,Object> completeSubmit = validatorContext.getSubmittedValues();}}
If the process definition is deployed as part of a ProcessApplication deployment, the validator instance is resolved using the process application classloader and / or the process application Spring Application Context / CDI Bean Manager, in case of an expression.
External Task Forms
If you want to call a task form that is not part of your application, you can add a reference to the desired form. The referenced task form will be configured in a way similar to the embedded task form. Open the properties view and enter as form key. The relevant XML tag looks like this:
Tasklist creates the URL by the pattern:
"../.." + contextPath (of process application) + "/" + "app" + formKey (from BPMN 2.0 XML) + "processDefinitionKey=" + processDefinitionKey + "&callbackUrl=" + callbackUrl;
When you have completed the task, the call back URL will be called.
How To
Generic Task Forms
The generic form will be used whenever you have not added a dedicated form for a UserTask or a .
Hit the Add a variable button to add a variable that will be passed to the process instance upon task completion. State a variable name, select the type and enter the desired value. Enter as many variables as you need.After hitting the Complete button, the process instance contains the entered values. Generic task forms can be very helpful during the development stage, so you do not need to implement all task forms before you can run a workflow. For debugging and testing this concept has many benefits as well.


