Advanced vector math
Unit vectors that are perpendicular to a surface (so, they describe the orientation of the surface) are called unit normal vectors. Though, usually they are just abbreviated as normals. Normals appear in planes, 3D geometry (to determine where each face or vertex is siding), etc. A normal is a unit vector, but it’s called normal because of its usage. (Just like we call (0,0) the Origin!).
It’s as simple as it looks. The plane passes by the origin and the surface of it is perpendicular to the unit vector (or normal). The side towards the vector points to is the positive half-space, while the other side is the negative half-space. In 3D this is exactly the same, except that the plane is an infinite surface (imagine an infinite, flat sheet of paper that you can orient and is pinned to the origin) instead of a line.
Now that it’s clear what a plane is, let’s go back to the dot product. The dot product between a unit vector and any point in space (yes, this time we do dot product between vector and position), returns the distance from the point to the plane:
GDScript
C#
But not just the absolute distance, if the point is in the negative half space the distance will be negative, too:
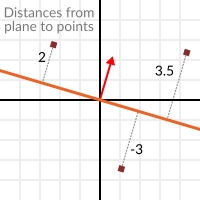
This allows us to tell which side of the plane a point is.
I know what you are thinking! So far this is nice, but real planes are everywhere in space, not only passing through the origin. You want real plane action and you want it now.
Remember that planes not only split space in two, but they also have polarity. This means that it is possible to have perfectly overlapping planes, but their negative and positive half-spaces are swapped.
With this in mind, let’s describe a full plane as a normal N and a distance from the origin scalar D. Thus, our plane is represented by N and D. For example:
For 3D math, Godot provides a built-in type that handles this.
Basically, N and D can represent any plane in space, be it for 2D or 3D (depending on the amount of dimensions of N) and the math is the same for both. It’s the same as before, but D is the distance from the origin to the plane, travelling in N direction. As an example, imagine you want to reach a point in the plane, you will just do:
GDScript
C#
var point_in_plane = N*D
var pointInPlane = N * D;
This will stretch (resize) the normal vector and make it touch the plane. This math might seem confusing, but it’s actually much simpler than it seems. If we want to tell, again, the distance from the point to the plane, we do the same but adjusting for distance:
GDScript
C#
var distance = N.dot(point) - D
var distance = N.Dot(point) - D;
The same thing, using a built-in function:
GDScript
var distance = plane.distance_to(point)
var distance = plane.DistanceTo(point);
This will, again, return either a positive or negative distance.
Flipping the polarity of the plane can be done by negating both N and D. This will result in a plane in the same position, but with inverted negative and positive half spaces:
GDScript
C#
N = -N;D = -D;
Of course, Godot also implements this operator in Plane, so doing:
GDScript
C#
var inverted_plane = -plane
var invertedPlane = -plane;
Will work as expected.
So, remember, a plane is just that and its main practical use is calculating the distance to it. So, why is it useful to calculate the distance from a point to a plane? It’s extremely useful! Let’s see some simple examples..
Planes clearly don’t come out of nowhere, so they must be built. Constructing them in 2D is easy, this can be done from either a normal (unit vector) and a point, or from two points in space.
In the case of a normal and a point, most of the work is done, as the normal is already computed, so just calculate D from the dot product of the normal and the point.
GDScript
C#
var N = normalvar D = normal.dot(point)
var N = normal;var D = normal.Dot(point);
For two points in space, there are actually two planes that pass through them, sharing the same space but with normal pointing to the opposite directions. To compute the normal from the two points, the direction vector must be obtained first, and then it needs to be rotated 90° degrees to either side:
GDScript
C#
# calculate vector from a to bvar dvec = (point_b - point_a).normalized()# rotate 90 degreesvar normal = Vector2(dvec.y, -dvec.x)# or alternatively# var normal = Vector2(-dvec.y, dvec.x)# depending the desired side of the normal
// calculate vector from a to bvar dvec = (pointB - pointA).Normalized();// rotate 90 degreesvar normal = new Vector2(dvec.y, -dvec.x);// or alternatively// var normal = new Vector2(-dvec.y, dvec.x);// depending the desired side of the normal
The rest is the same as the previous example, either point_a or point_b will work since they are in the same plane:
GDScript
C#
var N = normal;var D = normal.Dot(pointA);// this works the same// var D = normal.Dot(pointB);
Doing the same in 3D is a little more complex and will be explained further down.
Here is a simple example of what planes are useful for. Imagine you have a polygon. For example, a rectangle, a trapezoid, a triangle, or just any polygon where no faces bend inwards.
For every segment of the polygon, we compute the plane that passes by that segment. Once we have the list of planes, we can do neat things, for example checking if a point is inside the polygon.
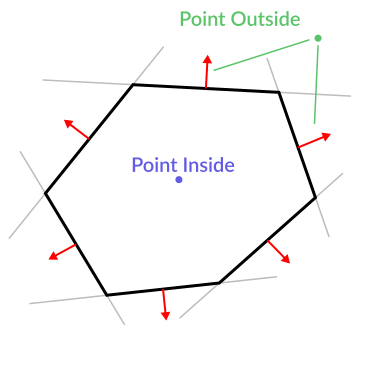
Code should be something like this:
GDScript
C#
var inside = truefor p in planes:# check if distance to plane is positiveif (p.distance_to(point) > 0):inside = falsebreak # with one that fails, it's enough
var inside = true;foreach (var p in planes){// check if distance to plane is positiveif (p.DistanceTo(point) > 0){inside = false;break; // with one that fails, it's enough}}
Pretty cool, huh? But this gets much better! With a little more effort, similar logic will let us know when two convex polygons are overlapping too. This is called the Separating Axis Theorem (or SAT) and most physics engines use this to detect collision.
With a point, just checking if a plane returns a positive distance is enough to tell if the point is outside. With another polygon, we must find a plane where all the other polygon points return a positive distance to it. This check is performed with the planes of A against the points of B, and then with the planes of B against the points of A:
Code should be something like this:
GDScript
C#
var overlapping = truefor p in planes_of_A:var all_out = truefor v in points_of_B:if (p.distance_to(v) < 0):all_out = falsebreakif (all_out):# a separating plane was found# do not continue testingoverlapping = falsebreakif (overlapping):# only do this check if no separating plane# was found in planes of Afor p in planes_of_B:var all_out = truefor v in points_of_A:if (p.distance_to(v) < 0):all_out = falsebreakif (all_out):overlapping = falsebreakif (overlapping):print("Polygons Collided!")
var overlapping = true;foreach (Plane plane in planesOfA){var allOut = true;foreach (Vector3 point in pointsOfB){if (plane.DistanceTo(point) < 0){allOut = false;break;}}if (allOut){// do not continue testingoverlapping = false;break;}if (overlapping){// only do this check if no separating plane// was found in planes of Aforeach (Plane plane in planesOfB){var allOut = true;foreach (Vector3 point in pointsOfA){if (plane.DistanceTo(point) < 0){allOut = false;break;}}if (allOut){overlapping = false;break;}}}if (overlapping){GD.Print("Polygons Collided!");}
As you can see, planes are quite useful, and this is the tip of the iceberg. You might be wondering what happens with non convex polygons. This is usually just handled by splitting the concave polygon into smaller convex polygons, or using a technique such as BSP (which is not used much nowadays).
Collision detection in 3D
This is another bonus bit, a reward for being patient and keeping up with this long tutorial. Here is another piece of wisdom. This might not be something with a direct use case (Godot already does collision detection pretty well) but it’s used by almost all physics engines and collision detection libraries :)
Remember that converting a convex shape in 2D to an array of 2D planes was useful for collision detection? You could detect if a point was inside any convex shape, or if two 2D convex shapes were overlapping.
Well, this works in 3D too, if two 3D polyhedral shapes are colliding, you won’t be able to find a separating plane. If a separating plane is found, then the shapes are definitely not colliding.
To refresh a bit a separating plane means that all vertices of polygon A are in one side of the plane, and all vertices of polygon B are in the other side. This plane is always one of the face-planes of either polygon A or polygon B.
In 3D though, there is a problem to this approach, because it is possible that, in some cases a separating plane can’t be found. This is an example of such situation:

To avoid it, some extra planes need to be tested as separators, these planes are the cross product between the edges of polygon A and the edges of polygon B
So the final algorithm is something like:
GDScript
C#
var overlapping = truefor p in planes_of_A:var all_out = truefor v in points_of_B:if (p.distance_to(v) < 0):all_out = falsebreakif (all_out):# a separating plane was found# do not continue testingoverlapping = falsebreakif (overlapping):# only do this check if no separating plane# was found in planes of Afor p in planes_of_B:var all_out = truefor v in points_of_A:if (p.distance_to(v) < 0):all_out = falsebreakif (all_out):overlapping = falsebreakif (overlapping):for ea in edges_of_A:for eb in edges_of_B:var n = ea.cross(eb)if (n.length() == 0):continuevar max_A = -1e20 # tiny numbervar min_A = 1e20 # huge number# we are using the dot product directly# so we can map a maximum and minimum range# for each polygon, then check if they# overlap.for v in points_of_A:var d = n.dot(v)max_A = max(max_A, d)min_A = min(min_A, d)var max_B = -1e20 # tiny numbervar min_B = 1e20 # huge numberfor v in points_of_B:var d = n.dot(v)max_B = max(max_B, d)min_B = min(min_B, d)if (min_A > max_B or min_B > max_A):# not overlapping!overlapping = falsebreakif (not overlapping):breakif (overlapping):print("Polygons collided!")
var overlapping = true;{var allOut = true;foreach (Vector3 point in pointsOfB){if (plane.DistanceTo(point) < 0){allOut = false;break;}}if (allOut){// a separating plane was found// do not continue testingoverlapping = false;break;}}if (overlapping){// only do this check if no separating plane// was found in planes of Aforeach (Plane plane in planesOfB){var allOut = true;foreach (Vector3 point in pointsOfA){if (plane.DistanceTo(point) < 0){allOut = false;break;}}if (allOut){overlapping = false;break;}}}if (overlapping){foreach (Vector3 edgeA in edgesOfA){foreach (Vector3 edgeB in edgesOfB){var normal = edgeA.Cross(edgeB);if (normal.Length() == 0){continue;}var maxA = float.MinValue; // tiny numbervar minA = float.MaxValue; // huge number// we are using the dot product directly// so we can map a maximum and minimum range// for each polygon, then check if they// overlap.foreach (Vector3 point in pointsOfA){var distance = normal.Dot(point);maxA = Mathf.Max(maxA, distance);minA = Mathf.Min(minA, distance);}var maxB = float.MinValue; // tiny numbervar minB = float.MaxValue; // huge numberforeach (Vector3 point in pointsOfB){var distance = normal.Dot(point);maxB = Mathf.Max(maxB, distance);minB = Mathf.Min(minB, distance);}if (minA > maxB || minB > maxA){// not overlapping!overlapping = false;break;}}if (!overlapping){break;}}}if (overlapping){}


